
Accurate blood pressure measurement
Accurate blood pressure measurement is crucial for managing cardiovascular health. This blog post explores the benefits of managing blood pressure more aggressively, the challenges with current measurement methods, and the potential for continuous monitoring devices.
Did you know that patients with hypertension should be reviewed every 9 months for their blood pressure?
Why monitoring your blood pressure is important
BP@Home is a scheme where you use a blood pressure monitor in the comfort of your own home to monitor your blood pressure and feedback the results to your GP surgery.
A blood pressure test checks if your blood pressure is healthy, or if it’s high or low. Blood pressure is the term used to describe the strength with which your blood pushes on the sides of your arteries as it’s pumped around your body. The medical term for high blood pressure is ‘hypertension’, which means your blood pressure is too high and your heart is working harder when pumping blood around your body.
Checking your blood pressure regularly and sharing the results with your GP practice can help your GP to understand your blood pressure. Your GP can then offer you advice and support to avoid serious problems, such as heart attacks, strokes and other health conditions.
Why you would be chosen to check your blood pressure
Your local GP Practice or a clinical staff member would have identified you as someone they would like to monitor their blood pressure at home. This may be because you:
- previously had a high blood pressure reading
- may have a health condition that puts you at risk of high
blood pressure - may have already been diagnosed with hypertension.
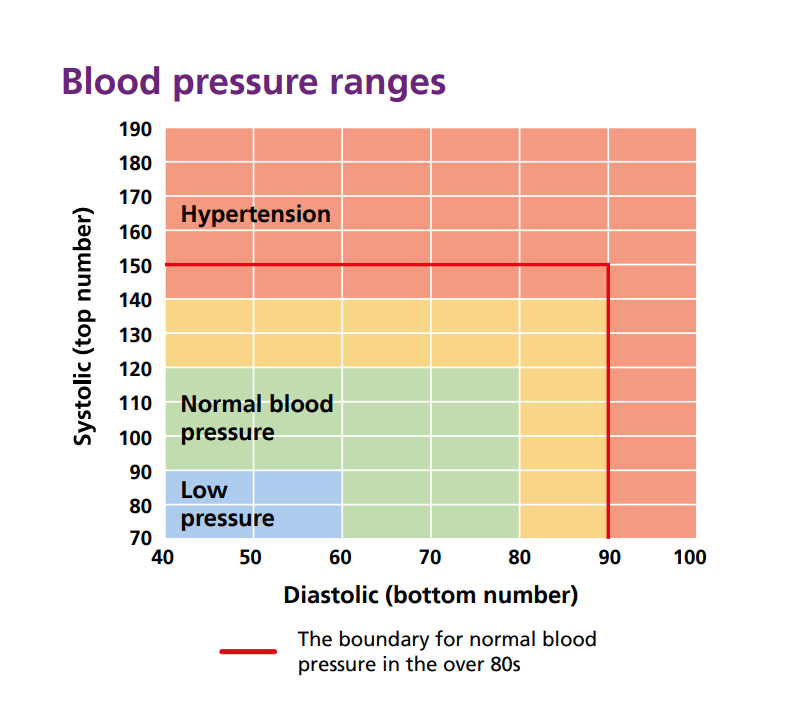
What is normal blood pressure?
Normal blood pressure is usually considered to be between 90/60 mmHg and 120/80 mmHg. For the over 80s, because it’s normal for arteries to get stiffer as we get older, the ideal blood pressure is under 150/90 mmHg (or 145/85 mmHg at home).
High-normal blood pressure is when you don’t have an ideal blood pressure, but you also don’t have hypertension. Being at this level might prompt you to explore ways to reduce your blood pressure to avoid developing high blood pressure in the future. Being at this level might prompt you to live a healthier lifestyle so you don’t develop high blood pressure.
When is it best to monitor your blood pressure?
It’s best to take your blood pressure readings with your monitor over four days, checking twice in the morning and twice at night. You can agree with your GP how and when you’ll give the readings to the GP practice.
- over 4 days
- twice in the morning and twice at night
- avoid a meal or exercise before
- avoid caffeine and nicotine before

How to monitor your blood pressure
It’s really important to monitor your blood pressure correctly, as this could impact your readings.
- Sit in comfortable position with your legs uncrossed and your back supported.
- Place the cuff 2-3cm above the elbow. Place it directly on the skin if possible.
- The cuff’s tubing should be at the centre of your arm on the front side.
- Your forearm should be supported at heart level.
- Take a reading. Take a second reading after a few minutes as the first is often high.
- Note and send your readings to your GP practice at the end of the four days.
Watch our instructive video below and find other helpful resources to manage your blood pressure.
Alternatively you can ask your GP for more information.
What happens next?
After you submit your BP recordings to your GP, the clinical staff will enter these on to your medical records to help them keep track of your health. If no further monitoring or testing is needed you may not hear from your GP, however if they would like to follow up with you, they will contact you to make an appointment.
In this appointment you may discuss your next steps to improving your blood pressure, which could include a referral for support – such as: weight management services, stop smoking support and other relevant lifestyle programmes. Your clinical team may recommend that medication is needed to support your blood pressure. Remember everyone is different and what works well for another person may not work well for you.
Ways to reduce high blood pressure
Below are some of the ways you can reduce your blood pressure and stay healthy. You can find more information on reducing risks of high blood pressure by scanning the QR code on the previous page.
- Get active
- Stop smoking
- Reduce alcohol
- Eat a balanced diet
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Reduce salt intake
- Attend NHS 40+ Health checks
- Take time to relax and de-stress
- Take medication
Benefits of aggressive blood pressure management
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a prevalent health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a silent killer, often showing no noticeable symptoms until it leads to serious complications such as heart attacks and strokes. However, recent data has shown that managing blood pressure within the recommended range of 120 over 80 can significantly reduce the risk of these life-threatening events.
Aggressive blood pressure management involves striving to keep blood pressure levels within the optimal range through various lifestyle modifications and, if necessary, medication. The benefits of adopting such an approach to hypertension management are numerous and can lead to better overall cardiovascular health.
Reduced risk of heart attacks and strokes
One of the most significant advantages of aggressive blood pressure management is the substantial reduction in the risk of heart attacks and strokes. The latest studies have indicated that maintaining blood pressure levels within the recommended range of 120 over 80 can reduce the occurrence of these cardiovascular events by up to 50%. This is a remarkable statistic that highlights the importance of keeping blood pressure under control.
An increased blood pressure puts strain on the arteries and other blood vessels, causing them to become narrower and less flexible. Over time, this can lead to the formation of clots, which can block blood flow to the heart or brain, resulting in a heart attack or stroke. By aggressively managing blood pressure, individuals can significantly reduce the strain on their cardiovascular system and lower the risk of these potentially fatal events.
Better overall cardiovascular health
Another key benefit of aggressive blood pressure management is improved overall cardiovascular health. High blood pressure is closely linked to various heart-related conditions, including heart failure, coronary artery disease, and kidney disease. By maintaining blood pressure within the optimal range, individuals can effectively reduce the risk of developing these conditions.
Consistently high blood pressure puts undue stress on the heart, increasing the workload it has to endure. Over time, this can lead to heart muscle damage and weaken the heart’s ability to pump blood effectively. Aggressive blood pressure management helps alleviate this stress, enabling the heart to function optimally and reducing the likelihood of heart-related complications.
Long-term well-being
While hypertension may seem like a manageable condition, its long-term consequences can be severe. Uncontrolled high blood pressure can contribute to the development of other chronic health conditions, such as diabetes, kidney disease, and even dementia. It is, therefore, crucial to maintain blood pressure within the optimal range to safeguard long-term well-being.
By adopting an aggressive approach to blood pressure management, individuals can proactively mitigate their risk of developing these associated health conditions. Regular monitoring, healthy lifestyle choices, and appropriate medication can all contribute to achieving and maintaining optimal blood pressure levels.
The benefits of aggressive blood pressure management cannot be overstated. By keeping blood pressure within the recommended range, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of heart attacks and strokes, improve their overall cardiovascular health, and safeguard their long-term well-being. It is essential to prioritise blood pressure management as a key aspect of maintaining a healthy lifestyle and reducing the possibility of severe complications.
Considering your weight is important as well to lead a healthy lifestyle.
Visit this link about weight management if you would like help to maintain a healthy weight.
Challenges with current blood pressure measurement
Measuring blood pressure accurately is crucial in determining an individual’s cardiovascular health. However, there are several challenges associated with the current methods of blood pressure measurement. In this article, we will explore some of these challenges and discuss potential solutions.
Doctor’s office measurements can sometimes be misleading
One of the main challenges with blood pressure measurement is the potential for misleading readings in a doctor’s office. This phenomenon, commonly known as “white coat hypertension” or “white coat syndrome,” refers to the tendency for a patient’s blood pressure to be higher when measured in a medical setting compared to their everyday life.
This discrepancy occurs due to a variety of factors, including anxiety, stress, and the unfamiliar environment of the doctor’s office. As a result, individuals may receive a falsely elevated blood pressure reading, leading to underdiagnosed cases of high blood pressure.
To mitigate this challenge, it is important for healthcare professionals to consider the potential effect of white coat hypertension when interpreting blood pressure readings. Additionally, patients can monitor their blood pressure at home using an appropriate device to obtain more accurate readings.
Sitting quietly for five minutes before measurement
Another challenge in blood pressure measurement is the importance of sitting quietly for five minutes before taking a reading. This period of rest allows the body to relax and stabilise, ensuring a more accurate portrayal of the individual’s blood pressure.
In some cases, healthcare providers may overlook this crucial step and measure blood pressure immediately upon the patient’s arrival. This can lead to inaccurate readings, potentially resulting in misdiagnosis or unnecessary medical interventions.
To overcome this challenge, healthcare professionals should prioritise the five-minute rest period before measuring blood pressure. By allowing the patient to relax and acclimate to the environment, more accurate readings can be obtained.
Manual measurements using a cuff and stethoscope
While automated cuffs are commonly used in medical settings for blood pressure measurement, manual measurements using a cuff and stethoscope are considered more accurate. Manual measurements allow healthcare professionals to listen to the Korotkoff sounds, which can provide additional information about the individual’s blood pressure.
Automated cuffs, on the other hand, rely solely on pressure sensors and algorithms to estimate blood pressure. Although these devices are convenient and widely available, they may not always provide the most precise readings.
Healthcare providers should consider utilising manual measurements with a cuff and stethoscope whenever possible, especially in situations where accuracy is paramount. These manual measurements can offer a more comprehensive assessment of the individual’s blood pressure status.
Accurate blood pressure measurement is crucial in diagnosing and managing high blood pressure. However, there are several challenges associated with the current methods of measurement. The tendency for misleading readings in a doctor’s office, the importance of sitting quietly for five minutes before measurement, and the potential inaccuracies of automated cuffs all contribute to the complexity of this process.
By addressing these challenges and implementing best practices, healthcare professionals can ensure more reliable blood pressure measurements and ultimately improve patient care and outcomes.
Self-measurement at home
In today’s fast-paced world, taking care of one’s health has become increasingly important. Regular check-ups and monitoring various health parameters are crucial in maintaining a healthy lifestyle. One such important parameter is blood pressure, and individuals can now conveniently check their own blood pressure at home using a manual cuff and stethoscope.
Using a manual cuff and stethoscope
A manual blood pressure cuff, also known as a sphygmomanometer, is a device used to measure blood pressure. It consists of an inflatable cuff that is wrapped around the upper arm and connected to a pressure gauge. A stethoscope is used in conjunction with the cuff to listen for the sounds of blood flow.
When measuring blood pressure at home, it is important to follow the correct procedure. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Find a quiet and comfortable place to sit.
- Expose the upper arm and rest it on a flat surface.
- Wrap the cuff around the upper arm, just above the elbow.
- Inflate the cuff by squeezing the pump bulb until it reaches a pressure of about 180 mmHg.
- Slowly release the pressure by opening the valve on the cuff while listening with the stethoscope.
- As the pressure drops, the first sound of blood flow, known as the systolic pressure, will be heard.
- Continue to decrease the pressure until the sound disappears, which indicates the diastolic pressure.
- Record the systolic and diastolic pressures.
By following this procedure, individuals can accurately measure their blood pressure at home.
Recording readings for further analysis
Patients who measure their blood pressure at home are advised to record their readings twice a day for two weeks. This data allows for further analysis and monitoring of blood pressure patterns. By tracking blood pressure over time, individuals and healthcare professionals can identify any significant changes or abnormalities that may require medical attention.
When recording blood pressure readings, it is important to note the date, time, and posture (sitting or standing) in addition to the actual blood pressure values. This additional information provides a comprehensive picture of an individual’s blood pressure throughout the day.
Conclusion
In conclusion, self-measurement of blood pressure at home using a manual cuff and stethoscope is a convenient and cost-effective method for monitoring one’s cardiovascular health. By following the correct procedure and investing in good quality equipment, individuals can obtain accurate readings. Recording these readings over a period of time allows for further analysis and early detection of any potential health issues. Regular self-monitoring empowers individuals to take control of their own health and make informed decisions about their well-being.
The future of blood pressure monitoring
Blood pressure monitoring plays a crucial role in managing cardiovascular health. Traditionally, this has involved periodic visits to a healthcare professional to measure blood pressure using a cuff-based device. However, advancements in technology are revolutionising this process, making it more convenient and accurate. In this article, we will explore the future of blood pressure monitoring, including the development of continuous monitoring devices and their potential integration into annual health check-ups.
Continuous monitoring devices
New technologies are being developed to provide continuous blood pressure monitoring, offering a more comprehensive understanding of an individual’s cardiovascular health. One such innovation is the wristband blood pressure monitor. This device, worn on the wrist like a regular wristwatch, utilises sensors to measure blood pressure continuously throughout the day. The data collected by these devices can be analysed to identify patterns, track changes over time, and provide real-time feedback.
Continuous monitoring devices offer several advantages over traditional cuff-based devices. They provide a more holistic view of blood pressure fluctuations, capturing variations that might be missed during infrequent measurements. Moreover, they are non-invasive and user-friendly, making them more practical for regular use. The data collected by these devices can be easily synced with smartphones or other devices for convenient monitoring and analysis.
Researchers and developers are also exploring other innovative approaches to continuous blood pressure monitoring, such as smart clothing embedded with sensors or implantable devices. These technologies aim to provide even more accurate and seamless monitoring, further enhancing the management of cardiovascular health.
Integration into annual health check-ups
Annual health check-ups are an important component of preventive healthcare, allowing individuals to assess their overall well-being and identify potential health issues early on. Currently, these check-ups typically involve measurements of various vital signs, such as heart rate, body temperature, and weight. However, blood pressure measurement is usually limited to a single reading taken during the visit.
The integration of continuous blood pressure monitoring into annual health check-ups could significantly enhance the effectiveness of these assessments. By collecting data over an extended period, healthcare professionals would gain a more accurate understanding of an individual’s blood pressure profile. This information could help identify potential hypertension or other cardiovascular issues that may otherwise go undetected.
Furthermore, continuous monitoring devices could enable individuals to actively participate in their own cardiovascular health management. By tracking their blood pressure on a regular basis, people can become more aware of the impact of their lifestyle choices and make informed decisions about their health. This empowerment and engagement can lead to better overall outcomes and a more proactive approach to managing cardiovascular health.
The potential for revolutionising cardiovascular health management
The advancements in continuous blood pressure monitoring have the potential to revolutionise how we manage cardiovascular health. By providing a more comprehensive and detailed understanding of blood pressure patterns, individuals and healthcare professionals can take proactive measures to prevent and manage hypertension and other cardiovascular conditions.
This new approach to blood pressure monitoring may lead to personalised interventions, such as targeted lifestyle modifications, medication adjustments, or timely medical interventions. With continuous monitoring devices, individuals can track the effectiveness of these interventions in real-time, allowing for adjustments as needed.
Moreover, the integration of continuous blood pressure monitoring into regular healthcare routines could contribute to a shift from reactive to proactive healthcare. Preventive measures, such as early detection and lifestyle modifications, can help reduce the burden of cardiovascular diseases on individuals and healthcare systems.
In conclusion
Blood pressure monitoring is evolving with the development of continuous monitoring devices like wristbands. These devices offer convenient and accurate measurements throughout the day, providing a more comprehensive understanding of an individual’s cardiovascular health. Continuous monitoring could become an integral part of annual health check-ups, enabling healthcare professionals to gather more accurate data and individuals to actively participate in their own health management. These advancements have the potential to revolutionise how we approach cardiovascular health by enabling personalised interventions and proactive preventive measures.
Visit the Mid and South Essex ICS website via this link for more information on blood pressure.

